Comment on In vivo assessment of bone quality in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes. [J Bone Miner Res. 2014] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24496824 J Bone Miner Res. 2014 Apr;29(4):784-6. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2189.
Monthly Archives: July 2018
Abstract Bisphosphonates (BPs) and denosumab reduce the risk of spine and nonspine fractures. Atypical femur fractures (AFFs) located in the subtrochanteric region and diaphysis of the femur have been reported in patients taking BPs and in patients on denosumab, but they also occur in patients with no exposure to these […]
Abstract Angiogenesis and osteogenesis are critically linked, although the role of angiogenesis is not well understood in osteogenic mechanical loading. In this study, either damaging or non-damaging cyclic axial compression was used to generate woven bone formation (WBF) or lamellar bone formation (LBF), respectively, at the mid-diaphysis of the adult […]
Abstract Evidence indicating that adult type 2 diabetes (T2D) is associated with increased fracture risk continues to mount. Unlike osteoporosis, diabetic fractures are associated with obesity and normal to high bone mineral density, two factors that are typically associated with reduced fracture risk. Animal models will likely play a critical […]
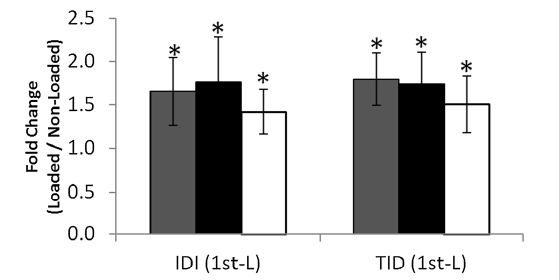
Abstract The reference point indentation (RPI) method is a microindentation technique involving successive indentation cycles. We employed RPI to measure average stiffness (Ave US), indentation distance increase (IDI), total indentation distance (TID), average energy dissipated (Ave ED), and creep indentation distance (CID) of swine femoral cortical bone (mid-diaphysis) as a […]
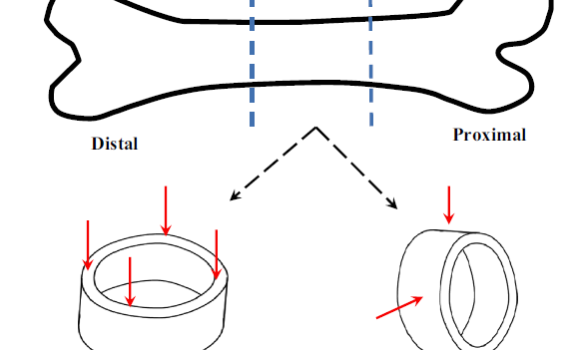
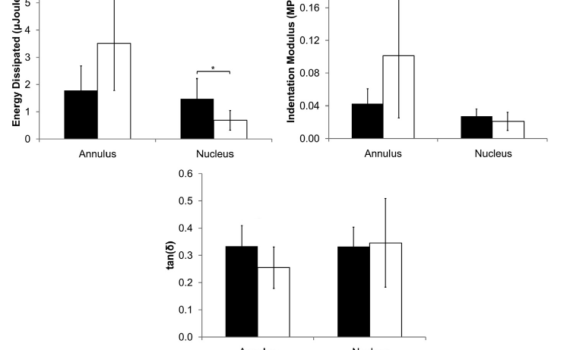
Abstract BACKGROUND CONTEXT: It is well-established that disc mechanical properties degrade with degeneration. However, prior studies utilized cadaveric tissues from donors with undefined back pain history. Disc degeneration may present with pain at the affected motion segment, or it may be present in the absence of back pain. The mechanical […]
Abstract Raloxifene treatment has been shown previously to positively affect bone mechanical properties following 1 year of treatment in skeletally mature dogs. Reference point indentation (RPI) can be used for in vivo assessment of mechanical properties and has been shown to produce values that are highly correlated with properties derived […]
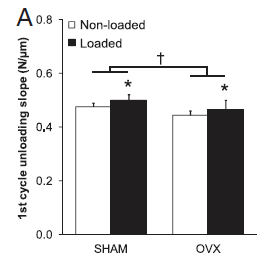
Abstract Exercise that mechanically loads the skeleton is advocated when young to enhance lifelong bone health. Whether the skeletal benefits of elevated loading when young persist into adulthood and after menopause are important questions. This study investigated the influence of a surgically induced menopause in female Sprague-Dawley rats on the […]
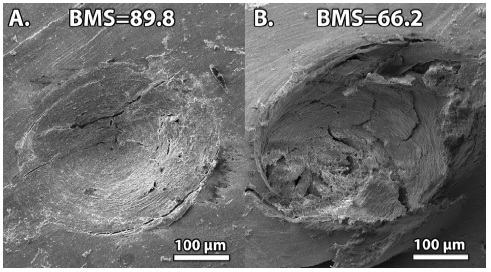
Abstract A novel, hand-held Reference Point Indentation (RPI) instrument, measures how well the bone of living patients and large animals resists indentation. The results presented here are reported in terms of Bone Material Strength, which is a normalized measure of how well the bone resists indentation, and is inversely related […]
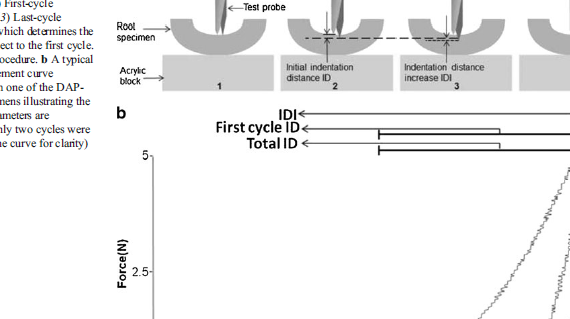
Abstract OBJECTIVES: The aim of this study was to investigate the capability of a novel reference point indentation apparatus to test the indentation properties of root canal surface dentine treated with three intracanal medicaments used in endodontic regeneration. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Immature human premolars were selected (n = 22). Four […]