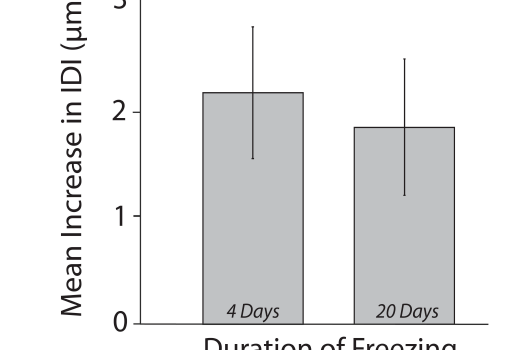
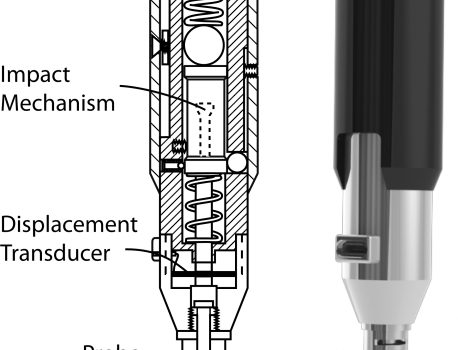
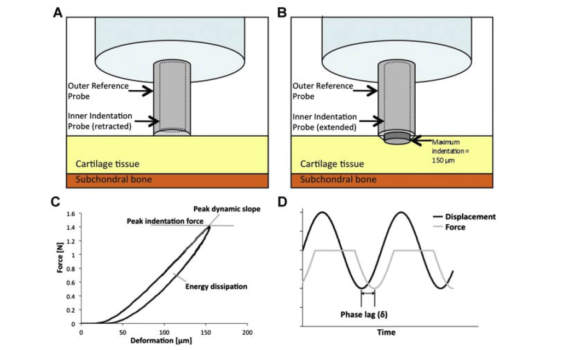
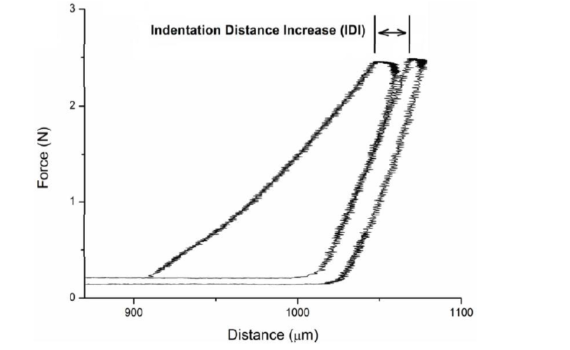
Abstract he serious health risks posed by bone fractures create a growing need for accurately diagnosing fracture risk. The Reference Point Indentation instrument (RPI) directly measures key mechanical properties in vivo to assess bone fracturability. There is a wealth of information that could be obtained from measuring cryopreserved bone samples […]
Yearly Archives: 2018
Abstract Here we describe a novel, hand-held reference point indentation (RPI), instrument that is designed for clinical measurements of bone material properties in living patients. This instrument differs from previous RPI instruments in that it requires neither a reference probe nor removal of the periosteum that covers the bone, thus […]
Abstract The objective of this study is to examine the local relationship between T(1ρ) relaxation times and the mechanical behavior of human osteoarthritic articular cartilage using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and local in situ microindentation. Seven human tibial plateaus were obtained from patients who underwent total knee arthroplasty due […]
ABSTRACT Characterization of bone is important as it aids in the understanding of bone pathologies and their corresponding treatments. Assessment of cortical bone morphology has been identified as an important aspect of overall bone quality as it contributes significantly to the mechanical strength of bone. In the first part of […]
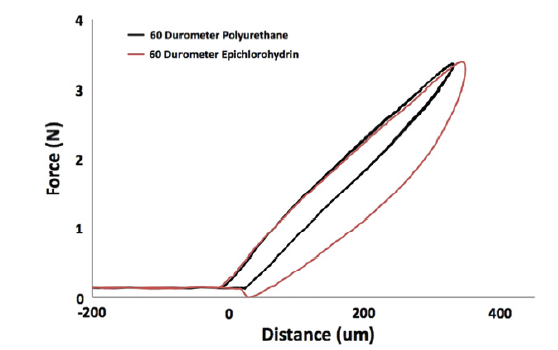
Abstract An understanding of the mechanical behavior of polymers is critical towards the design, implementation, and quality control of such materials. Yet experiments and method for the characterization of material properties of polymers remain challenging due the need to reconcile constitutive assumptions with experimental conditions. Well-established modes of mechanical testing, […]
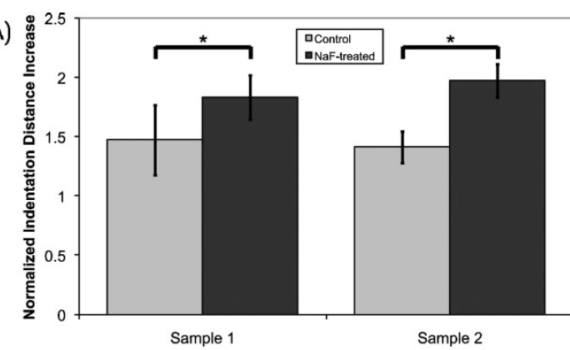
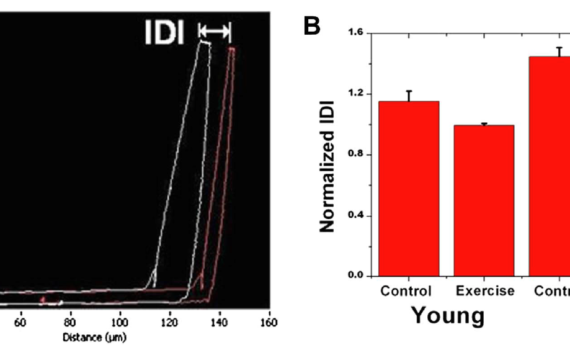
Abstract High doses of sodium fluoride in bones lead to severe softening, by weakening interfacial properties between the inorganic minerals and the organic components, while leaving mineralization unchanged. This leads to reduction of microdamage and associated stress‐whitening pointing to a change in failure mode. Accordingly, elastic modulus, failure stress, and […]
Abstract Here we describe modifications that allow the bone diagnostic instrument (BDI) [P. Hansma et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79, 064303 (2008); Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77, 075105 (2006)], developed to test human bone, to test the femora of mice. These modifications include reducing the effective weight of the instrument on […]
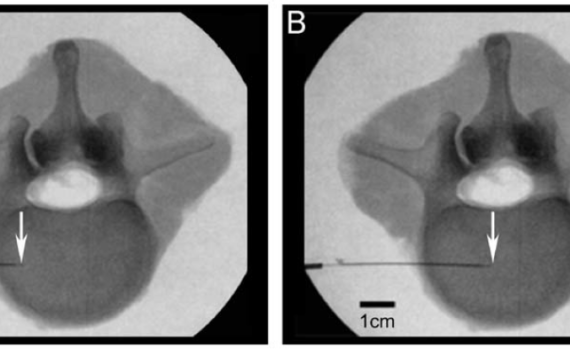
Abstract Despite recent advances in imaging diagnostic technology and additional treatment options our ability to prevent or inhibit discogenic back pain has not drastically improved. The challenge of linking early degenerative patterns to dysfunction and pain remains. Using a novel material testing device designated the Tissue Diagnostic Instrument (TDI) we […]
Abstract The bone diagnostic instrument (BDI) is being developed with the long-term goal of providing a way for researchers and clinicians to measure bone material properties of human bone in vivo. Such measurements could contribute to the overall assessment of bone fragility in the future. Here, we describe an improved […]
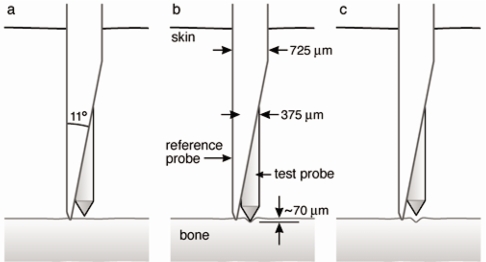
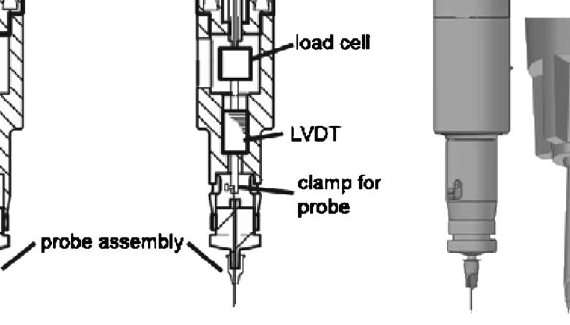
ABSTRACT The bone diagnostic instrument is designed to measure materials properties of bone even if it is covered with soft tissue such as periosteum, connective tissueand skin. It uses (1) a probe assembly, consisting of a reference probe that penetrates soft tissue and stops on the surface of the bone and a test probe that is inserted into the bone, (2) an actuation […]