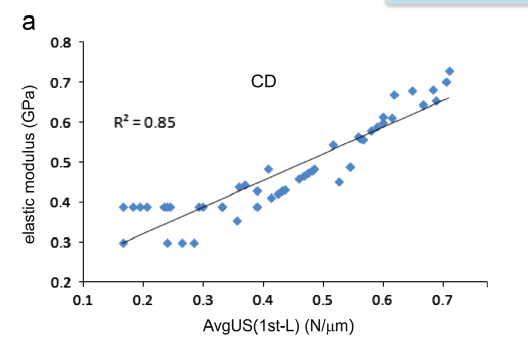
Abstract To unravel the origins of decreased bone strength in the superolateral femoral neck, we assessed bone structural features across multiple length scales at this cortical fracture initiating region in postmenopausal women with hip fracture and in aged-matched controls. Our combined methodological approach encompassed atomic force microscopy (AFM) characterization of […]
rpiresearch
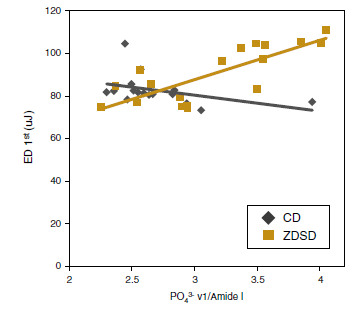
Abstract Diabetes detrimentally affects the musculoskeletal system by stiffening the collagen matrix due to increased advanced glycation end products (AGEs). In this study, tibiae and tendon from Zucker diabetic Sprague-Dawley (ZDSD) rats were compared to Sprague-Dawley derived controls (CD) using Atomic Force Microscopy. ZDSD and CD tibiae were compared using […]
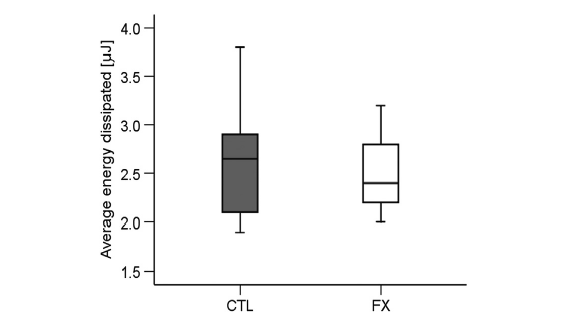
Abstract Osteogenesis imperfecta is a congenital disease commonly characterized by brittle bones and caused by mutations in the genes encoding Type I collagen, the single most abundant protein produced by the body. The oim model has a natural collagen mutation, converting its heterotrimeric structure (two α1 and one α2 chains) […]
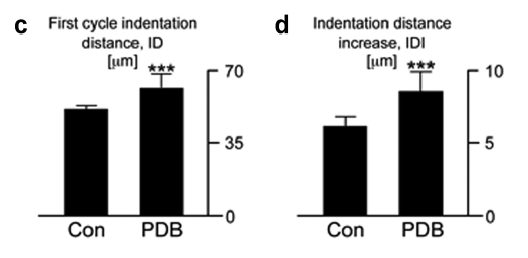
Abstract Paget’s disease of bone (PDB) is the second most common bone disease mostly developing after 50 years of age at one or more localized skeletal sites; it is associated with severely high bone turnover, bone enlargement, bowing/deformity, cracking, and pain. Here, to specifically address the origins of the deteriorated […]
Abstract While insulin-like growth factor I is a well-known anabolic agent in bone evidence is beginning to accumulate that its homologue, insulin, also has some anabolic properties for bone. There is specific evidence that insulin may work to stimulate osteoblast differentiation, which in turn would enhance production of osteocalcin, the osteoblast-produced peptide […]
Abstract To improve bone strength prediction beyond limitations of assessment founded solely on the bone mineral component, we investigated the effect of hyperlipidemia, present in more than 40% of osteoporotic patients, on multiscale structure of murine bone. Our overarching purpose is to estimate bone strength accurately, to facilitate mitigating fracture […]
Abstract Cells that form bone (osteoblasts) express both ephrinB2 and EphB4, and previous work has shown that pharmacological inhibition of the ephrinB2/EphB4 interaction impairs osteoblast differentiation in vitro and in vivo. The purpose of this study was to determine the role of ephrinB2 signaling in the osteoblast lineage in the […]
Abstract Anti-resorptive and anabolic agents are often prescribed for the treatment of osteoporosis continuously or sequentially for many years. However their impact on cortical bone quality and bone strength is not clear. Methods Six-month old female rats were either sham operated or ovariectomized (OVX). OVX rats were left untreated for […]
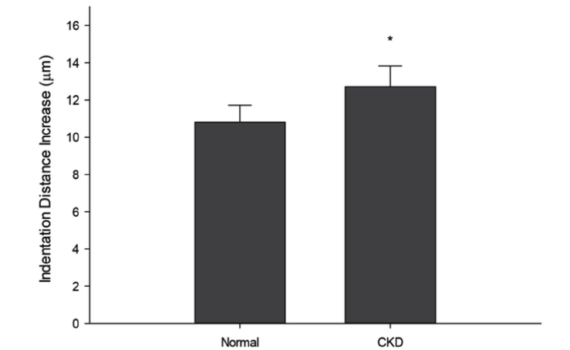
Abstract Chronic kidney disease (CKD), which leads tocortical bone loss and increasedporosity,increases therisk of fracture. Animal models have confirmed that these changes compromise whole bone mechanical properties. Estimates from whole bone testing suggest that material properties are negatively affected, though tissue-level assessmentshavenot been conducted. Therefore, the goal of the present […]
Abstract Osteoporosis is a silent disease, characterized by a porous bone micro-structure that enhances risk for fractures and associated disabilities. Senile, or age-related osteoporosis (SO), affects both men and women, resulting in increased morbidity and mortality. However, cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying senile osteoporosis are not fully known. Recent studies […]