We would like to thank Allen and colleagues for their thorough review of reference point indentation (RPI) for assessing bone mechanical properties in vivo.(1) The authors have focused on two separate RPI devices, the BioDent® and the OsteoProbe®, and have gone to great lengths to compare and contrast these instruments, which differ considerably […]
OsteoProbe
Abstract OBJECTIVE: To compare results obtained with a handheld reference point indentation instrument for bone material strength index (BMSi) measurements in the equine third metacarpal bone for various testing conditions. SAMPLE: 24 third metacarpal bones. PROCEDURES: Third metacarpal bones from both forelimbs of 12 horses were obtained. The dorsal surface […]
Abstract Diabetes and osteoporosis are both common diseases with increasing prevalences in the aging population. There is increasing evidence corroborating an association between diabetes mellitus and bone. This review will discuss the disease complications of diabetes on the skeleton, highlighting findings from epidemiological, molecular, and imaging studies in animal models […]
Abstract Although low bone mineral density (BMD) is strongly associated with increased fracture risk, up to 50% of those who suffer fractures are not detected as high-risk patients by BMD testing. Thus, new approaches may improve identification of those at increased risk for fracture by in vivo assessment of altered […]
Abstract Type 1 collagen matrix volume, its degree of completeness of its mineralization, the extent of collagen crosslinking and water content, and the non-collagenous proteins like osteopontin and osteocalcin comprise the main constituents of bone’s material composition. Each influences material strength and change in different ways during advancing age, health, […]
Abstract Deformations of vertebrae and sudden fractures of long bones caused by essentially normal loading are a characteristic problem in osteoporosis. If the loading is normal, then the explanation for and prediction of unexpected bone failure lies in understanding the mechanical properties of the whole bone-which come from its internal […]
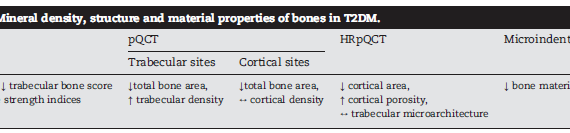
Abstract Increased fracture risk, traditionally associated with type 1 diabetes, has lately been of great concern in patients with type 2 diabetes. A variable increase in fracture risk has been reported, ranging from 20% to 3-fold, depending on skeletal site, diabetes duration and study design. Longer disease duration, the presence […]
Abstract Bone fragility has emerged as a new complication of diabetes. Several mechanisms in diabetes may influence bone homeostasis by impairing the action between osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes and/or changing the structural properties of the bone tissue. Some of these mechanisms can potentially alter the fate of mesenchymal stem cells, […]
Comment on Sclerostin deficiency is linked to altered bone composition. [J Bone Miner Res. 2014] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25158054 J Bone Miner Res. 2014 Oct;29(10):2141-3. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2346.
Abstract While insulin-like growth factor I is a well-known anabolic agent in bone evidence is beginning to accumulate that its homologue, insulin, also has some anabolic properties for bone. There is specific evidence that insulin may work to stimulate osteoblast differentiation, which in turn would enhance production of osteocalcin, the osteoblast-produced peptide […]