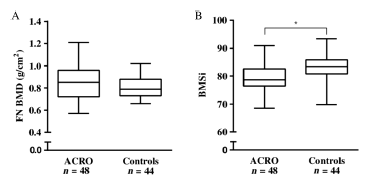
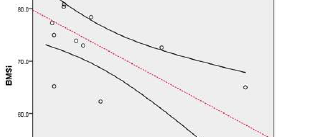
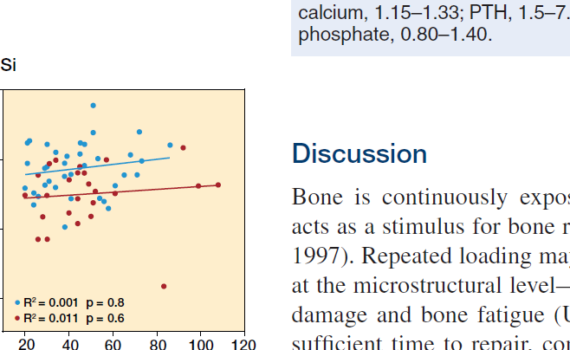
Abstract OBJECTIVE: Acromegaly is a rare disease caused by excess growth hormone (GH) production by the pituitary adenoma. The skeletal complications of GH and IGF-1 excess include increased bone turnover, increased cortical bone mass and deteriorated microarchitecture of trabecular bone, associated with a high risk of vertebral fractures in the […]
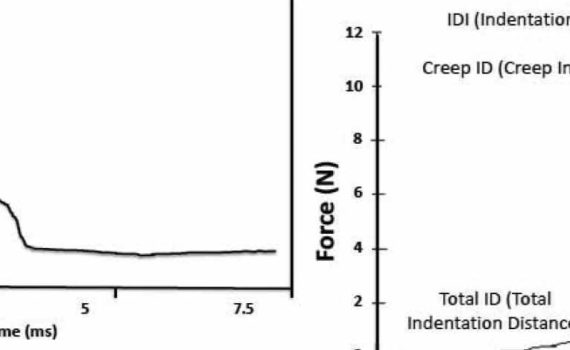
OsteoProbe
Abstract Gaucher disease (GD), one of the most common lysosomal disorders (a global population incidence of 1:50,000), is characterized by beta-glucocerebrosidase deficiency. Some studies have demonstrated bone infiltration in up to 80% of patients, even if asymptomatic. Bone disorder remains the main cause of morbidity in these patients, along with […]
Abstract Osteoporosis is defined as a reduction in bone mass and impairment of bone quality that lead to bone fragility and fracture risk. Bone quality includes a hierarchy of properties from macroscopic to nanoscale level. Several techniques have been developed in an attempt to measure these non-density properties. Densitometry, high-resolution […]
Abstract Background and purpose — Bone fragility is determined by bone mass, bone architecture, and the material properties of bone. Microindentation has been introduced as a measurement method that reflects bone material properties. The pathogenesis of underlying stress fractures, in particular the role of impaired bone material properties, is still […]
Abstract Low bone mineral density (BMD) in HIV-infected individuals has been documented in an increasing number of studies. However, it is not clear whether it is the infection itself or the treatment that causes bone impairment. Microindentation measures bone material strength (Bone Material Strength index) directly. We recruited 85 patients, […]
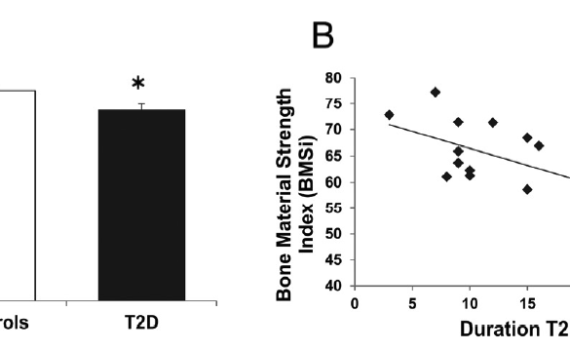
Abstract CONTEXT: Skeletal deterioration, leading to an increased risk of fracture, is a known complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D). Yet plausible mechanisms to account for skeletal fragility in T2D have not been clearly established. OBJECTIVE: The objective of the study was to determine whether bone material properties, as […]
Abstract Densitometry and imaging techniques are currently used in clinical settings to measure bone quantity and spatial structure. Recently, Reference Point Indentation has opened the possibility of directly assessing the mechanical characteristics of cortical bone in living individuals, adding a new dimension to the assessment of bone strength. Impact microindentation […]
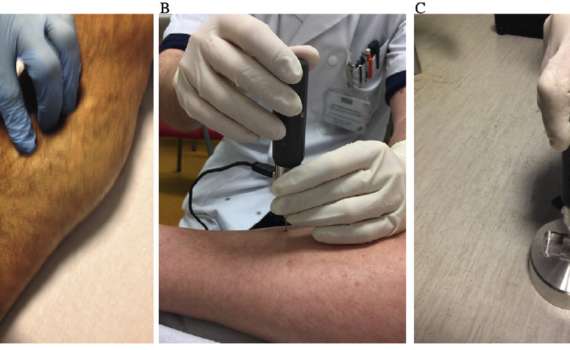
Abstract Impact microindentation is a novel method for measuring the resistance of cortical bone to indentation in patients. Clinical use of a handheld impact microindentation technique is expanding, highlighting the need to standardize the measurement technique. Here, we describe a detailed standard operation procedure to improve the consistency and comparability of the measurements […]
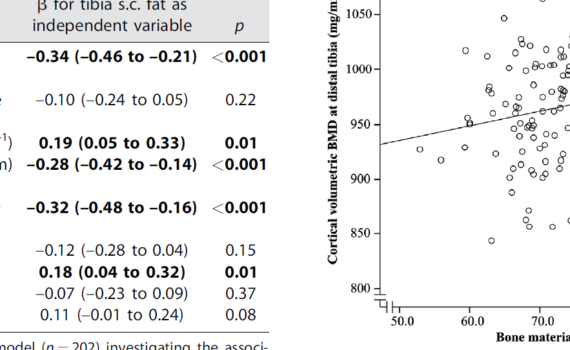
Abstract Obesity is associated with increased risk of fractures, especially at skeletal sites with a large proportion of cortical bone, such as the humerus and ankle. Obesity increases fracture risk independently of BMD, indicating that increased adipose tissue could have negative effects on bone quality. Microindentation assesses bone material strength […]
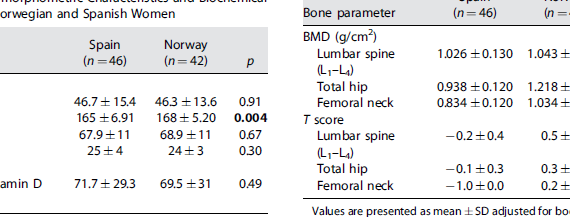
Abstract Hip fracture rates in Norway rank among the highest in the world, more than double that of Spanish women. Previous studies were unable to demonstrate significant differences between the two populations with respect to bone mass or calcium metabolism. In order to test whether the difference in fracture propensity […]