Abstract Gap junctions are formed from ubiquitously expressed proteins called connexins that allow the transfer of small signaling molecules between adjacent cells. Gap junctions are especially important for signaling between osteocytes and other bone cell types. The most abundant type of connexin in bone is connexin 43 (Cx43). The C-terminal […]
bone
Abstract Reference Point Indentation (RPI) is a novel microindentation tool that has emerging clinical potential for the assessment of fracture risk as well as use as a laboratory tool for straight-forward mechanical characterisation of bone. Despite increasing use of the tool, little research is available to advise the set-up of […]
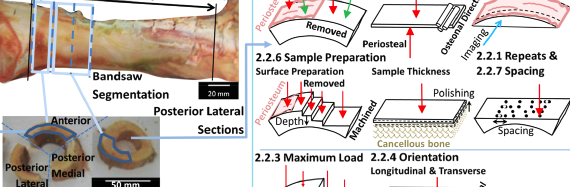
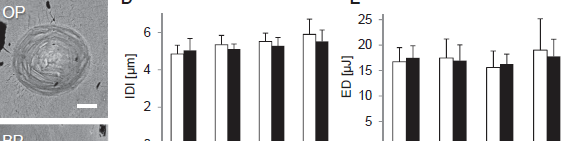
Abstract Characterization of bone’s hierarchical structure in aging, disease and treatment conditions is imperative to understand the architectural and compositional modifications to the material and its mechanical integrity. Here, cortical bone sections from 30 female proximal femurs – a frequent fracture site – were rigorously assessed to characterize the osteocyte […]
Abstract Although low bone mineral density (BMD) is strongly associated with increased fracture risk, up to 50% of those who suffer fractures are not detected as high-risk patients by BMD testing. Thus, new approaches may improve identification of those at increased risk for fracture by in vivo assessment of altered […]
Abstract While insulin-like growth factor I is a well-known anabolic agent in bone evidence is beginning to accumulate that its homologue, insulin, also has some anabolic properties for bone. There is specific evidence that insulin may work to stimulate osteoblast differentiation, which in turn would enhance production of osteocalcin, the osteoblast-produced peptide […]
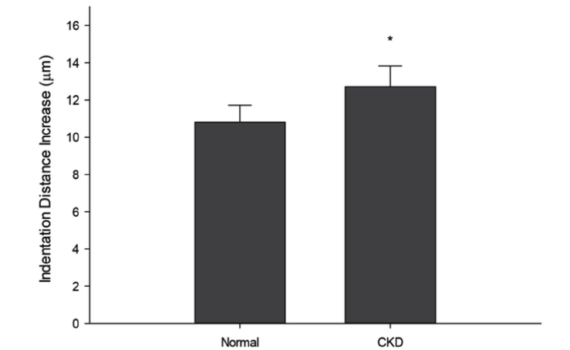
Abstract Chronic kidney disease (CKD), which leads tocortical bone loss and increasedporosity,increases therisk of fracture. Animal models have confirmed that these changes compromise whole bone mechanical properties. Estimates from whole bone testing suggest that material properties are negatively affected, though tissue-level assessmentshavenot been conducted. Therefore, the goal of the present […]
Abstract Evidence indicating that adult type 2 diabetes (T2D) is associated with increased fracture risk continues to mount. Unlike osteoporosis, diabetic fractures are associated with obesity and normal to high bone mineral density, two factors that are typically associated with reduced fracture risk. Animal models will likely play a critical […]
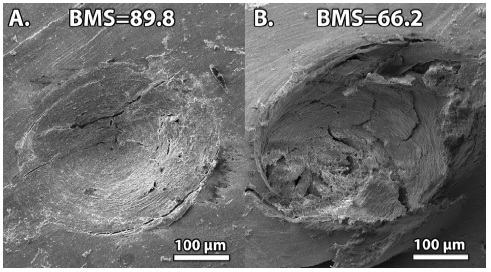
Abstract A novel, hand-held Reference Point Indentation (RPI) instrument, measures how well the bone of living patients and large animals resists indentation. The results presented here are reported in terms of Bone Material Strength, which is a normalized measure of how well the bone resists indentation, and is inversely related […]
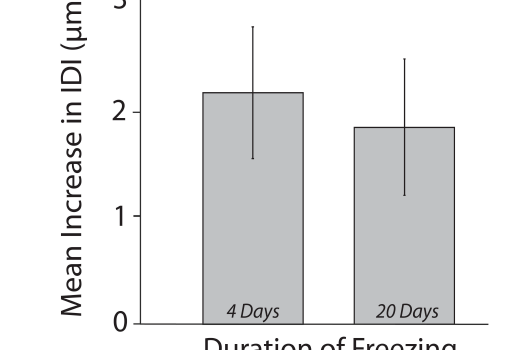
Abstract he serious health risks posed by bone fractures create a growing need for accurately diagnosing fracture risk. The Reference Point Indentation instrument (RPI) directly measures key mechanical properties in vivo to assess bone fracturability. There is a wealth of information that could be obtained from measuring cryopreserved bone samples […]
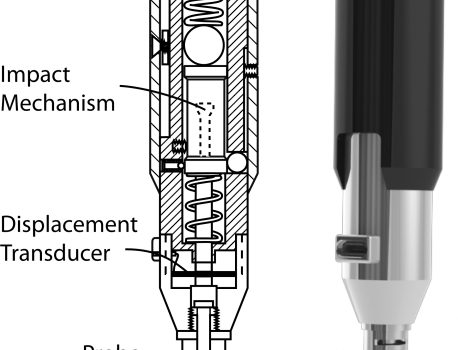
Abstract Here we describe a novel, hand-held reference point indentation (RPI), instrument that is designed for clinical measurements of bone material properties in living patients. This instrument differs from previous RPI instruments in that it requires neither a reference probe nor removal of the periosteum that covers the bone, thus […]