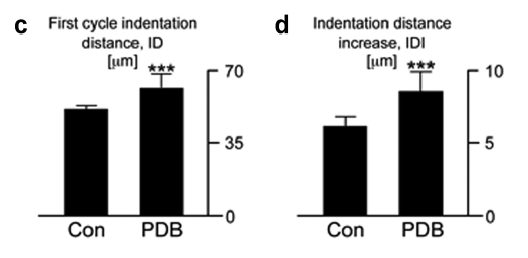
Abstract Paget’s disease of bone (PDB) is the second most common bone disease mostly developing after 50 years of age at one or more localized skeletal sites; it is associated with severely high bone turnover, bone enlargement, bowing/deformity, cracking, and pain. Here, to specifically address the origins of the deteriorated […]
Fracture risk
Abstract Evidence indicating that adult type 2 diabetes (T2D) is associated with increased fracture risk continues to mount. Unlike osteoporosis, diabetic fractures are associated with obesity and normal to high bone mineral density, two factors that are typically associated with reduced fracture risk. Animal models will likely play a critical […]
Abstract The aim of the study was to test, whether bone material strength differs between different subtypes of osteoporotic fracture and assess whether it relates to vertebral fracture severity. Cortical bone material strength index (BMSi) was measured by impact microindentation in 66 women with osteoporotic fracture and 66 age- and […]
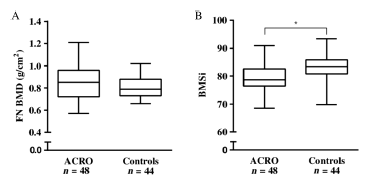
Abstract OBJECTIVE: Acromegaly is a rare disease caused by excess growth hormone (GH) production by the pituitary adenoma. The skeletal complications of GH and IGF-1 excess include increased bone turnover, increased cortical bone mass and deteriorated microarchitecture of trabecular bone, associated with a high risk of vertebral fractures in the […]
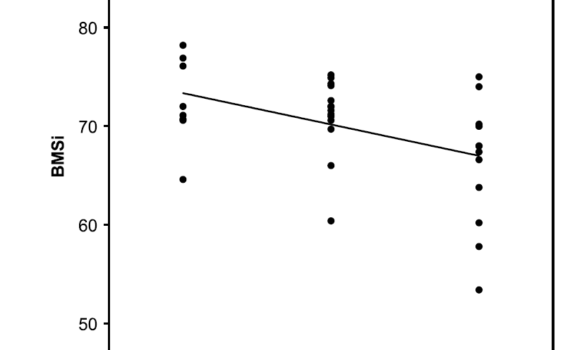
Abstract Background and purpose — Bone fragility is determined by bone mass, bone architecture, and the material properties of bone. Microindentation has been introduced as a measurement method that reflects bone material properties. The pathogenesis of underlying stress fractures, in particular the role of impaired bone material properties, is still […]
Abstract Low bone mineral density (BMD) in HIV-infected individuals has been documented in an increasing number of studies. However, it is not clear whether it is the infection itself or the treatment that causes bone impairment. Microindentation measures bone material strength (Bone Material Strength index) directly. We recruited 85 patients, […]
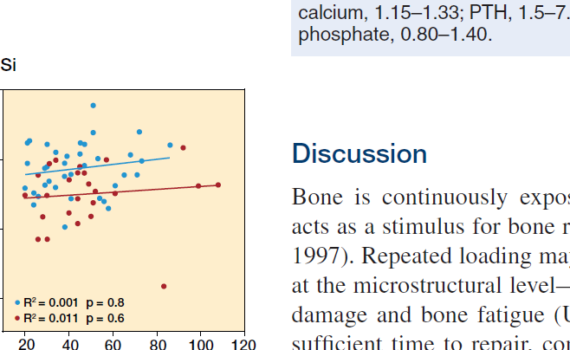
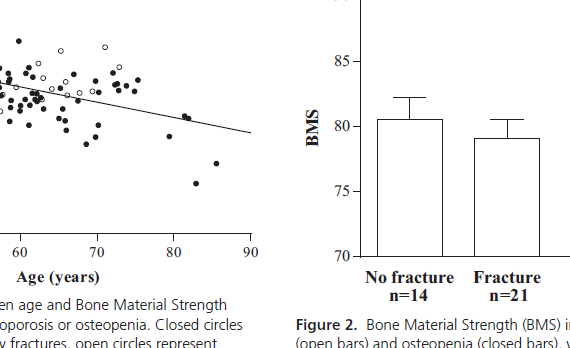
Abstract CONTEXT: Bone mineral density (BMD) does not fully capture fracture risk as the majority of fractures occur in patients with osteopenia, suggesting that altered bone material properties and changes in microarchitecture may contribute to fracture risk. OBJECTIVE: This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between bone material strength (BMS), […]
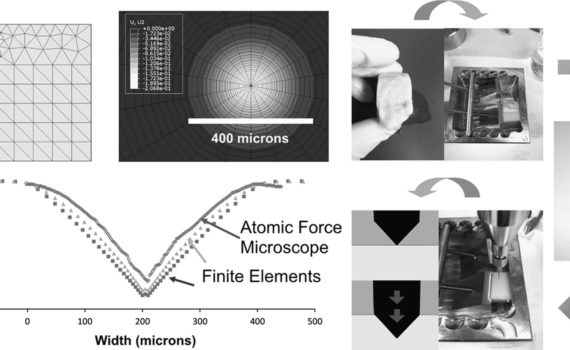
Abstract In an attempt to study the mechanical behavior of bone under indentation, methods of analyses and experimental validations have been developed, with a selected test material. The test material chosen is from an equine cortical bone. Stress-strain relationships are first obtained from conventional mechanical property tests. A finite element […]
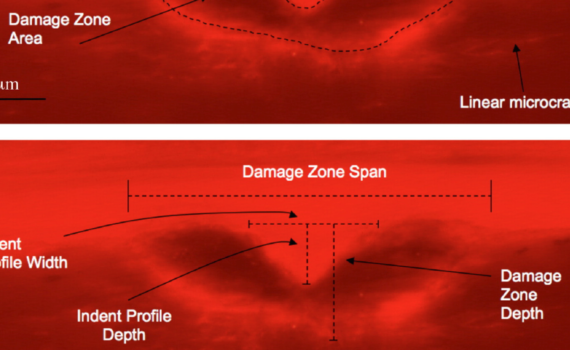
Abstract The likelihood of suffering a bone fracture is not solely predicated on areal bone mineral density. As people age, there are numerous changes to the skeleton occurring at multiple length scales (from millimeters to submicron scales) that reduce the ability of bone to resist fracture. Herein is a review […]
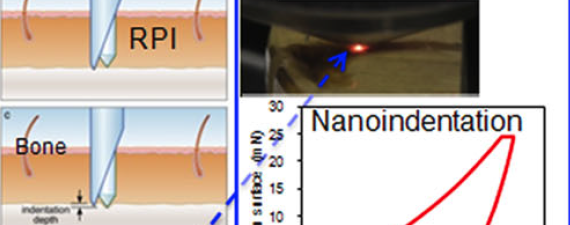
Abstract Measurement of bone mineral density (BMD) is the clinical gold standard in cases of compromised skeletal integrity, such as with osteoporosis. While BMD is a useful measurement to index skeletal health, it is also limited since it cannot directly assess any mechanical properties. The ability to directly assess mechanical […]