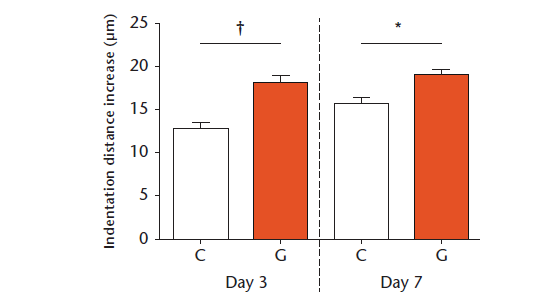
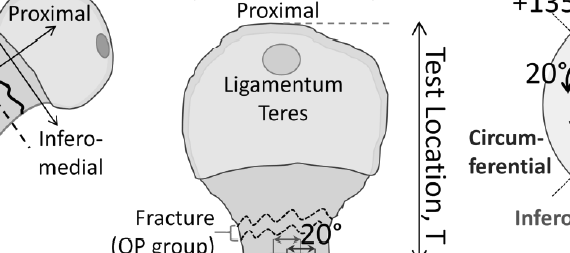
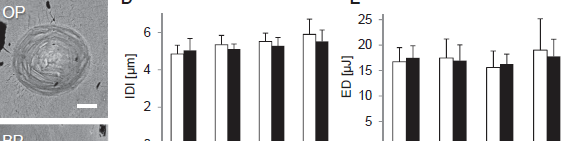
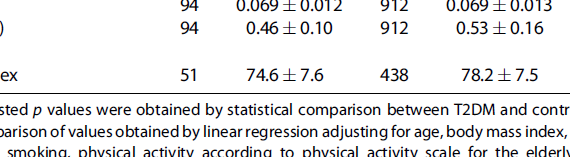Abstract OBJECTIVES: Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) are a post-translational modification of collagen that form spontaneously in the skeletal matrix due to the presence of reducing sugars, such as glucose. The accumulation of AGEs leads to collagen cross-linking, which adversely affects bone quality and has been shown to play a major […]
Osteoporosis
Abstract In contrast to traditional approaches to fracture risk assessment using clinical risk factors and bone mineral density (BMD), a new technique, reference point microindentation (RPI), permits direct assessment of bone quality; in vivo tibial RPI measurements appear to discriminate patients with a fragility fracture from controls. However, it is […]
Abstract The global trend towards increased longevity has resulted in ageing populations and a rise in diseases or conditions that primarily affect older persons. One such condition is osteoporosis (fragile or porous bones), which causes an increased fracture risk. Vertebral and hip fractures lead to increased morbidity and mortality and […]
Abstract Characterization of bone’s hierarchical structure in aging, disease and treatment conditions is imperative to understand the architectural and compositional modifications to the material and its mechanical integrity. Here, cortical bone sections from 30 female proximal femurs – a frequent fracture site – were rigorously assessed to characterize the osteocyte […]
Abstract Age- and disease (osteoporotic fractured and osteoarthritic tissue)-related changes in the distribution of cortical bone were examined, using a multimodality approach, including measurement of local density, geometry and mechanical properties, where changes in these properties can give rise to instability and increasing probability of fracture. In contrast to the […]
Abstract Bone adapts to loading in several ways, including redistributing bone mass and altered geometry and microarchitecture. Because of previous methodological limitations, it is not known how the bone material strength is affected by mechanical loading in humans. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of a […]
Abstract We tested whether cortical bone tissue properties assessed by in vivo impact microindentation would distinguish postmenopausal women with recent distal radius (DRF) or hip fracture (HF) from nonfracture controls (CONT). We enrolled postmenopausal women with recent DRF (n = 57), HF (n = 41), or CONT (n = 93), and used impact microindentation to assess […]
Abstract Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with an increased risk of fractures according to several studies. The underlying mechanisms remain unclear, although small case-control studies indicate poor quality of the cortical bone. We have studied a population-based sample of women aged 75 to 80 years in Gothenburg, randomly […]
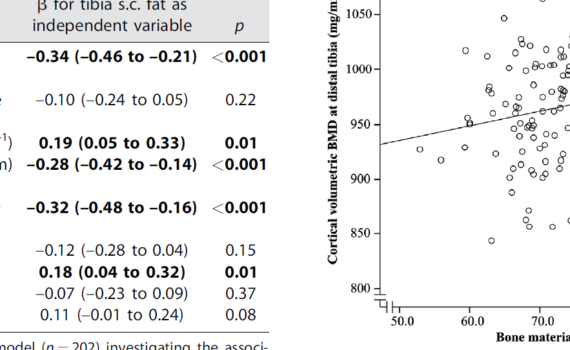
Abstract Obesity is associated with increased risk of fractures, especially at skeletal sites with a large proportion of cortical bone, such as the humerus and ankle. Obesity increases fracture risk independently of BMD, indicating that increased adipose tissue could have negative effects on bone quality. Microindentation assesses bone material strength […]
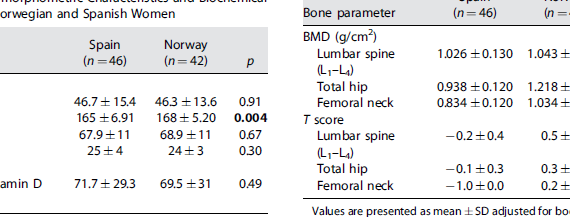
Abstract Hip fracture rates in Norway rank among the highest in the world, more than double that of Spanish women. Previous studies were unable to demonstrate significant differences between the two populations with respect to bone mass or calcium metabolism. In order to test whether the difference in fracture propensity […]