Abstract Type 2 diabetes (T2D) incidence in adolescents is rising and may interfere with peak bone mass acquisition. We tested the effects of early-onset T2D on bone mass, microarchitecture, and strength in the TALLYHO/JngJ mouse, which develops T2D by 8 weeks of age. We assessed metabolism and skeletal acquisition in […]
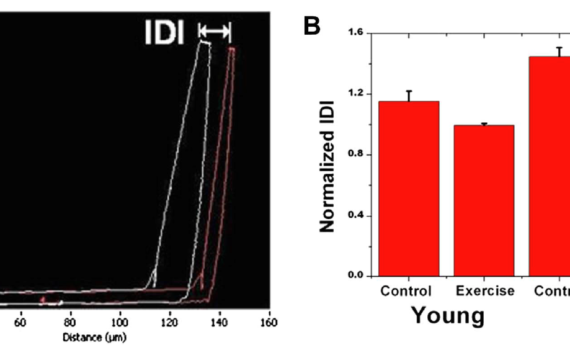
Reference point indentation
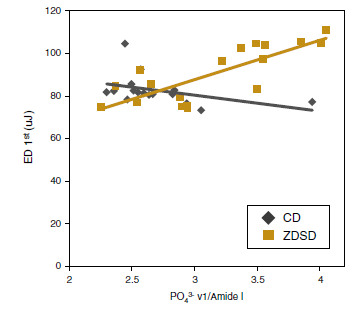
Abstract Diabetes detrimentally affects the musculoskeletal system by stiffening the collagen matrix due to increased advanced glycation end products (AGEs). In this study, tibiae and tendon from Zucker diabetic Sprague-Dawley (ZDSD) rats were compared to Sprague-Dawley derived controls (CD) using Atomic Force Microscopy. ZDSD and CD tibiae were compared using […]
Abstract Osteogenesis imperfecta is a congenital disease commonly characterized by brittle bones and caused by mutations in the genes encoding Type I collagen, the single most abundant protein produced by the body. The oim model has a natural collagen mutation, converting its heterotrimeric structure (two α1 and one α2 chains) […]
Comment on In vivo assessment of bone quality in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes. [J Bone Miner Res. 2014] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24496824 J Bone Miner Res. 2014 Apr;29(4):784-6. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2189.
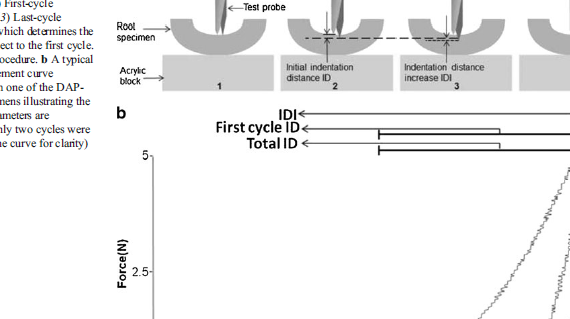
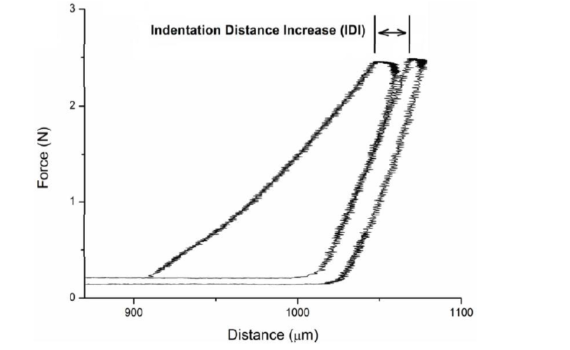
Abstract OBJECTIVES: The aim of this study was to investigate the capability of a novel reference point indentation apparatus to test the indentation properties of root canal surface dentine treated with three intracanal medicaments used in endodontic regeneration. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Immature human premolars were selected (n = 22). Four […]
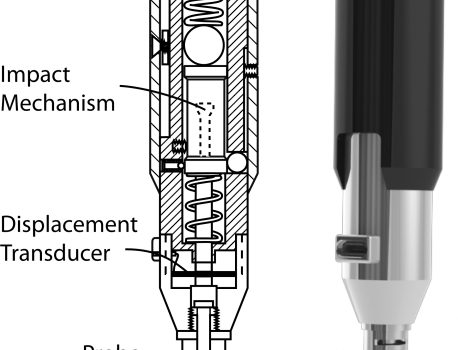
Abstract Here we describe a novel, hand-held reference point indentation (RPI), instrument that is designed for clinical measurements of bone material properties in living patients. This instrument differs from previous RPI instruments in that it requires neither a reference probe nor removal of the periosteum that covers the bone, thus […]
ABSTRACT Characterization of bone is important as it aids in the understanding of bone pathologies and their corresponding treatments. Assessment of cortical bone morphology has been identified as an important aspect of overall bone quality as it contributes significantly to the mechanical strength of bone. In the first part of […]
Abstract Here we describe modifications that allow the bone diagnostic instrument (BDI) [P. Hansma et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79, 064303 (2008); Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77, 075105 (2006)], developed to test human bone, to test the femora of mice. These modifications include reducing the effective weight of the instrument on […]
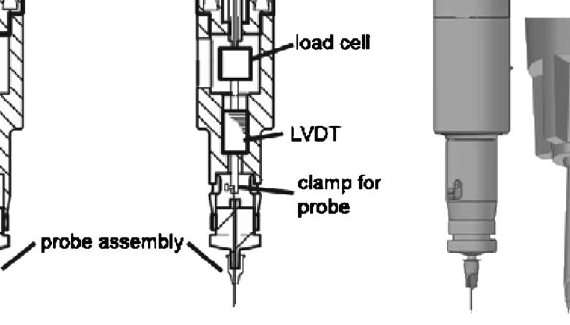
Abstract The bone diagnostic instrument (BDI) is being developed with the long-term goal of providing a way for researchers and clinicians to measure bone material properties of human bone in vivo. Such measurements could contribute to the overall assessment of bone fragility in the future. Here, we describe an improved […]
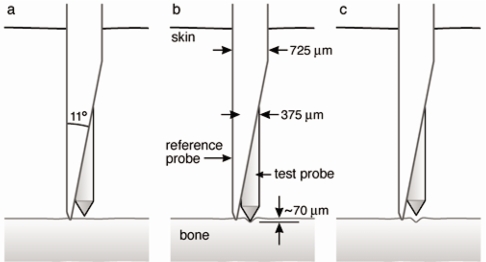
ABSTRACT The bone diagnostic instrument is designed to measure materials properties of bone even if it is covered with soft tissue such as periosteum, connective tissueand skin. It uses (1) a probe assembly, consisting of a reference probe that penetrates soft tissue and stops on the surface of the bone and a test probe that is inserted into the bone, (2) an actuation […]