Abstract BACKGROUND: Bone mineral density (BMD) measured by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry is used to assess bone health in kidney transplant recipients (KTR). Trabecular bone score and in vivo microindentation are novel techniques that directly measure trabecular microarchitecture and mechanical properties of bone at a tissue level and independently predict fracture […]
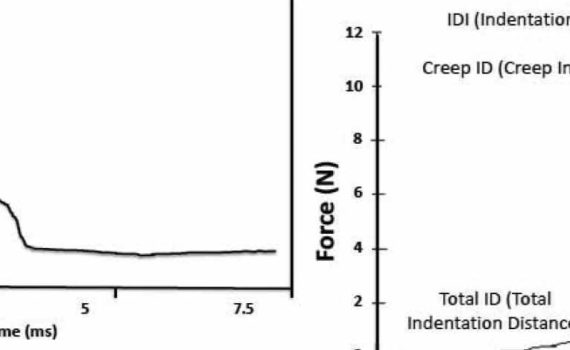
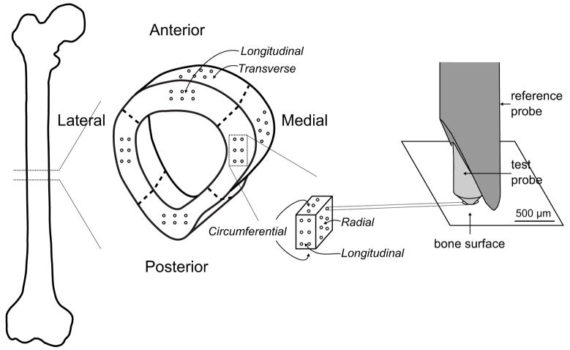
Reference point indentation
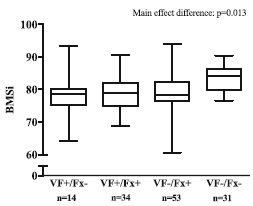
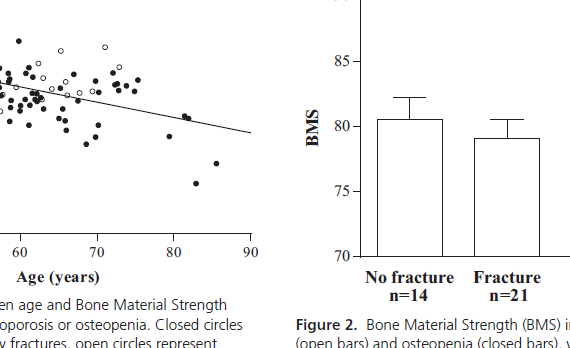
Abstract We evaluated the relationship between bone material strength index (BMSi) and fragility fractures, including vertebral fractures. Our data showed that BMSi is low in all fracture patients with low bone mass, independently of whether patients sustained a vertebral or a non-vertebral fracture. INTRODUCTION: Impact microindentation (IMI) is a new […]
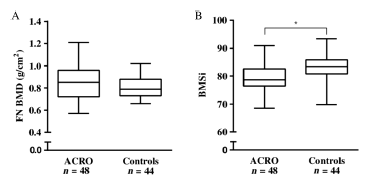
Abstract OBJECTIVE: Acromegaly is a rare disease caused by excess growth hormone (GH) production by the pituitary adenoma. The skeletal complications of GH and IGF-1 excess include increased bone turnover, increased cortical bone mass and deteriorated microarchitecture of trabecular bone, associated with a high risk of vertebral fractures in the […]
Abstract Background and purpose — Bone fragility is determined by bone mass, bone architecture, and the material properties of bone. Microindentation has been introduced as a measurement method that reflects bone material properties. The pathogenesis of underlying stress fractures, in particular the role of impaired bone material properties, is still […]
Abstract Low bone mineral density (BMD) in HIV-infected individuals has been documented in an increasing number of studies. However, it is not clear whether it is the infection itself or the treatment that causes bone impairment. Microindentation measures bone material strength (Bone Material Strength index) directly. We recruited 85 patients, […]
Abstract Densitometry and imaging techniques are currently used in clinical settings to measure bone quantity and spatial structure. Recently, Reference Point Indentation has opened the possibility of directly assessing the mechanical characteristics of cortical bone in living individuals, adding a new dimension to the assessment of bone strength. Impact microindentation […]
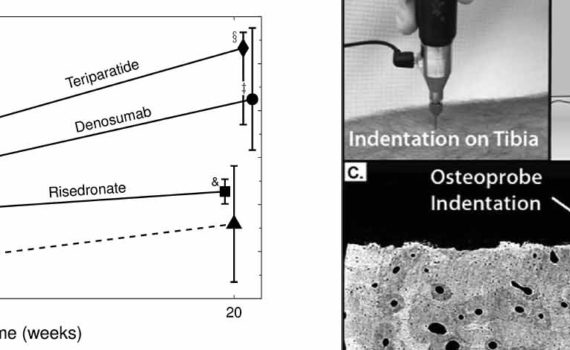
Abstract Glucocorticoids, widely used in inflammatory disorders, rapidly increase bone fragility and, therefore, fracture risk. However, common bone densitometry measurements are not sensitive enough to detect these changes. Moreover, densitometry only partially recognizes treatment-induced fracture reductions in osteoporosis. Here, we tested whether the reference point indentation technique could detect bone […]
Abstract CONTEXT: Bone mineral density (BMD) does not fully capture fracture risk as the majority of fractures occur in patients with osteopenia, suggesting that altered bone material properties and changes in microarchitecture may contribute to fracture risk. OBJECTIVE: This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between bone material strength (BMS), […]
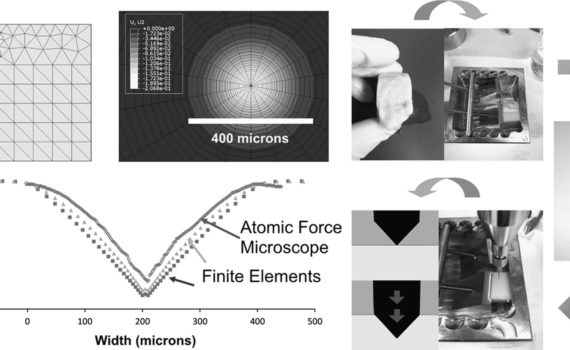
Abstract In an attempt to study the mechanical behavior of bone under indentation, methods of analyses and experimental validations have been developed, with a selected test material. The test material chosen is from an equine cortical bone. Stress-strain relationships are first obtained from conventional mechanical property tests. A finite element […]
Abstract Reference point indentation (RPI) is a microindentation technique involving 20 cycles of loading in “force-control” that can directly assess a patient׳s bone tissue properties. Even though preliminary clinical studies indicate a capability for fracture discrimination, little is known about what mechanical behavior the various RPI properties characterize and how […]